What You Need to Know About Radon
Radon is a naturally occurring, cancer-causing byproduct of the radioactive decay of Uranium in the soil. While you cannot see, smell or taste radon, it may still be a problem in your home. Breathing in radon-contaminated air increases your risk of getting lung cancer. In fact, radon is the leading cause of lung cancer amongst non-smokers in the United States.
Testing your home for radon is crucial to determine if you have a problem. While self-testing kits are available, home inspectors often use more reliable kits, ensuring accurate results. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established an “action level” of 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L) for indoor radon. If your home’s test results exceed this level, it’s recommended to take steps to mitigate the radon gas.
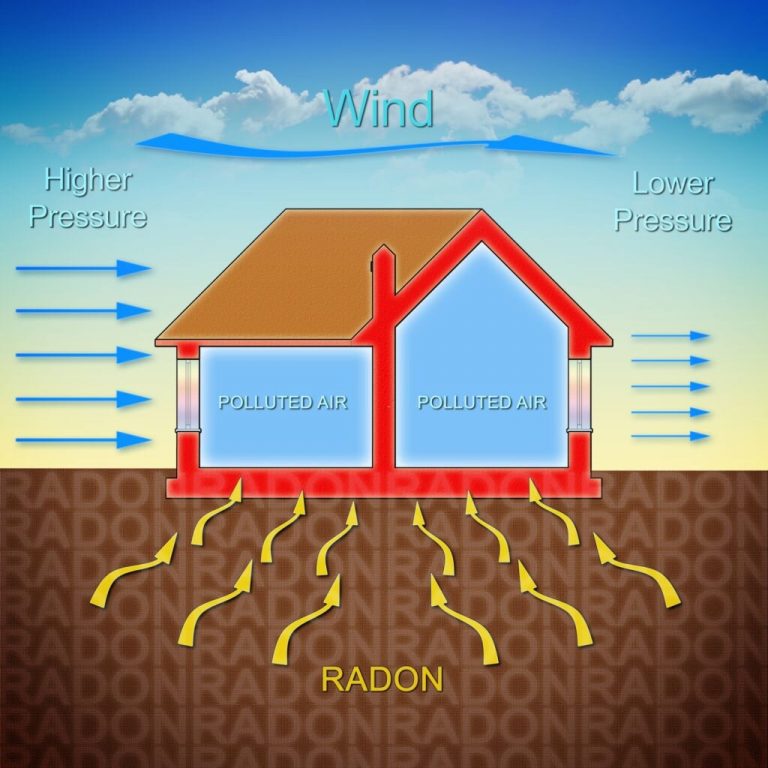
Radon can enter your home through various pathways due to the difference in air pressure between the soil and your home’s interior. The lower pressure inside draws radon in through cracks in the foundation, floor/wall joints, gaps around service pipes, and other openings. Additionally, radon can enter through well water, exposed soil in crawl spaces or around sumps, and even from building materials like brick, concrete, and rock.
Radon Insurance Coverage for Home Inspectors
Are you a home inspector looking for radon insurance coverage for your home inspector business? Inspectors who offer radon testing during home inspections and are covered by E&O insurance have a better chance of landing the inspection. Read on to learn about how to get certified to test for radon and more about the importance of having radon testing E&O insurance.
Learn more about Home Inspector Insurance
How does a Home Inspector Get Certified to Test for Radon?
If you are a home inspector and would like to become a certified radon tester and are not already a member of InterNACHI, one way to become certified is to join as a member. After that, you will have to complete the InterNACHI free, online Advanced Radon Measurement Service Provider Course and then follow the Continuing Education (CE) Policy for InterNACHI Certified Inspectors. If you are not a member of InterNACHI, there are other ways to be certified as well. For example, you can take the National Radon Safety Board’s certification exam. Some additional courses can be taken to become certified as well.
Benefits of Becoming a Radon Inspector
Wondering why you should become a radon inspector? There are many benefits that you will find rewarding. First, radon is considered to be the “silent killer” because it is an odorless, colorless radioactive gas that can lead to lung cancer. By becoming a radon inspector, you can help to protect clients from potentially being at risk for developing lung cancer. Next, becoming a radon inspector can help you to have an additional source of income. If radon testing is being requested in a home inspection and you are not certified to test for radon, then you will be losing business to other home inspectors that are certified.
What Tools or Equipment do Radon Inspectors Need?
There are not many tools/equipment that radon inspectors need, but perhaps the most important are continuous radon monitors. They sample the air in a home for at least 48 hours to check for the presence of radon, and then the monitor will show the average level of radon from all the samples that were taken. There are two types of tests that can be done using other types of radon monitors– short-term and long-term tests. Short-term test kits should stay in the tested building for anywhere from two to 90 days, and long-term tests will stay in the building being tested for more than 90 days. Long-term tests typically can give a more accurate reading that reflects the yearly average radon level within a building than short-term tests can.
Within the short-term testing, there are two different groups of devices that are most often used. The first is passive devices. These types of devices do not require power in order to work. Included in this group of devices are charcoal canisters, charcoal liquid scintillation detectors, and alpha track detectors.
The second group is active devices, which require power to work correctly. Within this group, there are many types of continuous monitors. These active monitors typically can supply data about the scope of differences within the given test period. Active testing usually is more expensive than passive testing.
Am I Liable If My Radon Inspection Tools Fail?
Having an E&O insurance policy should help to mitigate most claims filed due to failed inspection tools. However, most home inspector insurance policies do not include radon testing, so it is necessary to purchase a radon endorsement. An endorsement can either add or change coverage to your insurance policy. Having a radon endorsement is one of the most important things you can do to protect yourself against radon-related claims.
LEARN MORE ABOUT HOME INSPECTOR INSURANCE
Interested in Radon Insurance Coverage for Home Inspectors?
By working with EliteMGA, you can ensure that you have proper coverage for the services you provide. Give us a call today to discuss adding this endorsement to your policy. Or if you don’t have coverage with EliteMGA yet, apply now!!